Cholesterol is a term that often evokes concern, given its strong association with heart disease. Yet, not all cholesterol is harmful. Understanding “what is the difference between good and bad cholesterol?” is vital for maintaining a healthy heart and overall wellbeing. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the nuances of cholesterol, its types, and how they impact your health.
Introduction to Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in all the cells of your body. It is essential for the production of hormones, vitamin D, and substances that help digest foods. However, the body needs only a minimal amount to function properly. When cholesterol levels become unbalanced, health issues can arise.
What Is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol travels through the bloodstream in small packages called lipoproteins, which are made of fat (lipid) on the inside and proteins on the outside. There are two main types of lipoproteins to be aware of: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
The Role of Cholesterol
Before diving into “what is the difference between good and bad cholesterol?”, it’s essential to understand the role cholesterol plays in your body. Cholesterol aids in the formation of cell membranes, certain hormones, and vitamin D. The liver produces all the cholesterol your body needs, but it also comes from the food you eat, particularly animal products like meat, cheese, and eggs.
What Is the Difference Between Good and Bad Cholesterol?
To understand “what is the difference between good and bad cholesterol?”, it is crucial to differentiate between LDL and HDL.
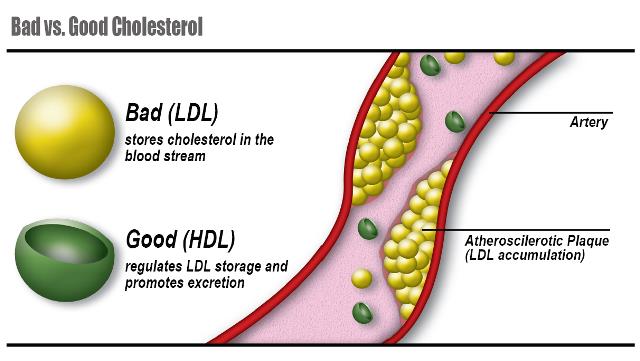
Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) – The Bad Cholesterol
Low-density lipoprotein, or LDL, is often referred to as “bad cholesterol.” High levels of LDL can lead to the build-up of cholesterol in your arteries. This accumulation, known as plaque, can narrow your arteries and make them less flexible, a condition called atherosclerosis. If a clot forms and blocks a narrowed artery, it can result in a heart attack or stroke.
High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) – The Good Cholesterol
High-density lipoprotein, or HDL, is known as “good cholesterol.” HDL helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream. It transports LDL cholesterol to the liver, where it can be processed and eliminated from the body. Higher levels of HDL are associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
Factors Affecting Cholesterol Levels
Understanding “what is the difference between good and bad cholesterol?” also involves recognising the factors that influence these levels.
Diet
Your diet significantly impacts your cholesterol levels. Foods high in saturated fats and trans fats can increase LDL cholesterol levels. Examples include:
- Red meat
- Full-fat dairy products
- Fried foods
- Processed snacks
Conversely, foods rich in unsaturated fats, fibre, and plant sterols can help increase HDL cholesterol and lower LDL cholesterol. These include:
- Fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel)
- Nuts and seeds
- Avocados
- Whole grains
- Fruits and vegetables
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol. Aerobic exercises such as walking, running, and cycling are particularly beneficial.
Weight Management
Being overweight or obese can raise your LDL cholesterol levels and lower your HDL cholesterol. Losing weight, even a small amount, can help improve your cholesterol profile.
Genetics
Your genetics play a role in determining your cholesterol levels. Familial hypercholesterolemia is an inherited condition that results in high LDL cholesterol levels.
Age and Sex
Cholesterol levels tend to rise with age. Before menopause, women usually have lower total cholesterol levels than men of the same age. However, after menopause, women’s LDL cholesterol levels often increase.
Diagnosing High Cholesterol
To effectively manage cholesterol, it is crucial to understand “what is the difference between good and bad cholesterol?” and how to diagnose high levels.
Lipid Panel
A lipid panel is a blood test that measures your total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. Triglycerides are another type of fat in the blood. High levels can also increase your risk of heart disease.
Ideal Cholesterol Levels
- Total cholesterol: Less than 200 mg/dL
- LDL cholesterol: Less than 100 mg/dL
- HDL cholesterol: 60 mg/dL or higher
- Triglycerides: Less than 150 mg/dL
Health Implications of Cholesterol Imbalance
Understanding “what is the difference between good and bad cholesterol?” is key to recognising the potential health implications of cholesterol imbalances.
Heart Disease
High LDL cholesterol levels can lead to the development of atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Cholesterol build-up can also affect the arteries that supply blood to your limbs, leading to peripheral arterial disease.
Diabetes
Diabetes can lower HDL cholesterol and raise LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Liver Disease
Excessive cholesterol can accumulate in the liver, leading to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Managing Cholesterol Levels
Knowing “what is the difference between good and bad cholesterol?” is crucial for managing your levels effectively.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes is often the first line of defence against high cholesterol.
- Diet: Adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Weight Loss: If you’re overweight, losing even a small amount of weight can improve your cholesterol levels.
Medications
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to lower cholesterol levels. Medications such as statins, bile acid sequestrants, and cholesterol absorption inhibitors can help.
Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of your cholesterol levels is essential. Your doctor can help you determine how often you should have your cholesterol checked.
Myths and Misconceptions About Cholesterol
To fully grasp “what is the difference between good and bad cholesterol?”, it’s important to dispel common myths and misconceptions.
Myth 1: All Cholesterol Is Bad
Not all cholesterol is bad. HDL cholesterol is beneficial and helps remove LDL cholesterol from your arteries.
Myth 2: You Can Feel High Cholesterol
High cholesterol typically has no symptoms. The only way to know your cholesterol levels is through a blood test.
Myth 3: Only Overweight People Have High Cholesterol
High cholesterol can affect anyone, regardless of their weight. Factors such as diet, genetics, and physical activity play significant roles.
Myth 4: You Don’t Need to Worry About Cholesterol Until You’re Older
Cholesterol levels can start to rise as early as childhood. It’s important to maintain healthy habits from a young age.
The Importance of Understanding Cholesterol
Understanding “what is the difference between good and bad cholesterol?” is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health. By knowing the roles of LDL and HDL cholesterol, you can make informed decisions about your diet, exercise, and overall lifestyle.
Early Education
Educating yourself and your family about cholesterol can lead to healthier choices and prevention of heart disease from a young age.
Proactive Health Management
Regular check-ups and blood tests allow for early detection and management of high cholesterol, reducing the risk of serious complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, “what is the difference between good and bad cholesterol?” is a vital question for anyone interested in maintaining heart health. LDL cholesterol, often termed “bad cholesterol,” can lead to plaque build-up in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease. Conversely, HDL cholesterol, known as “good cholesterol,” helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream, protecting against heart disease.
By understanding these differences, you can take proactive steps to manage your cholesterol levels through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and, if necessary, medications. Remember, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to keeping your cholesterol levels in check and ensuring long-term health and wellbeing. Regular monitoring and consultation with healthcare professionals can help you stay on track and make the best choices for your heart health.
This article was originally published on USA TAAZA TIME